- About
- Industries
- Products
- Wastewater Treatment
- Conventional Effluent Treatment: AQUASEP
- Toxic Refractory < 60,000 COD Removal: Catalytic Hydro-oxidation CHD-Ox
- Wet Air Oxidation for TOXIC > 60,000 COD : THERMOX
- Nanobubbles in Water Treatment: NANOPOREX-E
- Chemical-Free Cooling Tower Technology – A Sustainable Solution: ZEPHYR
- MVR for ZLD: Vapozem
- Membranes in wastewater Treatment: PROMEM
- TSS removal and Product recovery using Ceramics: PORESEP
- Heavy Metals and Trace Contaminant removal using Resins: SORBION
- Improving Efficiency of your sand bed filters: NANOMATRIX
- Choosing the Right technology for Wastewater treatment: Wastewater Treatability Studies’
- Reduce/Recover Oil from Wastewater: DISORB
- Produced Water Treatment: PWT
- Non Biofouling Membranes in wastewater Treatment: PROMEM-B
- Advanced Bioaugmentation Culture: BIOPORE
- Cavitation using Ultrasonics: RUSONICS-E
- Oxygen Generator System for Industries: OXYLIFE
- Process Solutions
- Precious Metal catalyst Filtration: CONTUFILT-M
- Activated Carbon Filtration: CONTUFILT-AC
- Raney Nickel Catalyst Filtration: CONTUFILT-RN
- Hot Gas Filtration: CONTUFILT – MH
- Biosolids removal using ceramics: PORESEP
- MVR for ZLD: VAPOZEM
- Ion Exchange-based RESINS: SORBION
- Dehydrating solvents by Zeolite Membranes: SOLVOSEP
- HiGee Continuous Distillation: ROTASEP
- Molecular Separation by Membranes: PROMEM
- Filtration & Separation
- Precious Metal catalyst Filtration: CONTUFILT – M
- Activated Carbon Filtration: CONTUFILT-AC
- Raney Nickel Catalyst Filtration: CONTUFILT-RN
- Hot Gas Filtration: CONTUFILT – MH
- Ceramic Dynamic Membrane Filtration: PORESEP
- MVR for ZLD: Vapozem
- Nano-Bubbles Improve Process Efficiency: NANOPOREX
- Alternate to Continuous Distillation / Rectification: ROTASEP
- Liquid-Liquid Extraction Mixer Settler: SEPARIX
- Ion Exchange-based RESINS: SORBION
- Pervaporation: Dehydrating Solvents and Separating Mixtures: SOLVOSEP
- Cartridges & Filter Bags: FLOWSEP™
- Molecular Separation by Membranes: Recovery and Isolation: PROMEM
- Colour / Organics / VOC Removal: CARBOSORB
- Oxygen Generator System for Industries: OXYLIFE
- RUSONIC – Sonochemistry
- Magnetic Separator Technology: MAG-Filt
- Wastewater Treatment
- Resource
- Contact Us
A comparison between aerobic and anaerobic wastewater treatment technology
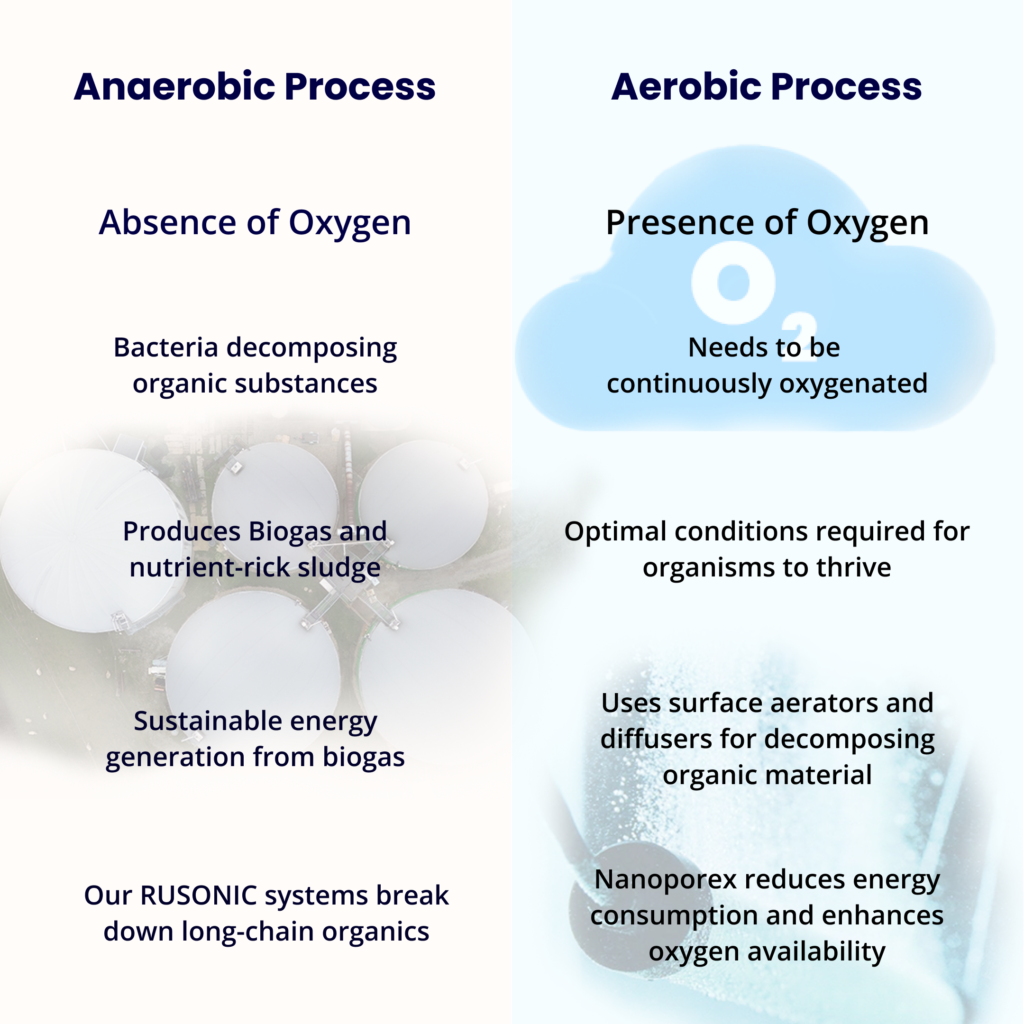
Ensuring public health requires effective wastewater treatment, with biological treatment being a key component among the primary treatment methods. Within biological treatment, two main approaches emerge: aerobic and anaerobic wastewater treatment. While anaerobic wastewater treatment or any aerobic treatment occurs without oxygen, aerobic treatment relies on oxygen for its processes.
Anaerobic Wastewater Treatment: Operating Without Oxygen
In anaerobic wastewater treatment, microorganisms break down organic material in the absence of oxygen. Anaerobic digestion, a common method in this treatment, involves bacteria decomposing organic substances to produce biogas and nutrient-rich sludge. Anaerobic digesters, which facilitate this process, come in various configurations such as complete mix, plug flow, and expanded granular sludge bed reactors.
Aerobic Wastewater Treatment: Oxygen-Dependent Processes
Introducing Oxygen: Aeration Techniques
Aerobic treatment methods utilize devices like surface aerators or diffusers to introduce oxygen into the water. Surface aerators churn wastewater mechanically, while diffusers release air bubbles from the tank bottom to enhance oxygen transport. These methods support oxygen-dependent bacteria and microorganisms in effectively decomposing organic material. Our latest innovation, Nanoporex – nanobubble generation, reduces energy consumption and enhances oxygen availability for bacteria in the aerobic process.
Harnessing Biogas: Advantages of Anaerobic Treatment

Diverse Devices, Shared Goals: Anaerobic Treatment Methods

Various anaerobic treatment devices like lagoons, sludge blanket reactors, and anaerobic filter reactors employ unique mechanisms for organic material degradation. Anaerobic treatment is favored for its cost-effectiveness, and potential soil enhancement through sludge, and biogas generation. Efficient methane release is crucial to mitigate environmental impact, often achieved through flaring. Anaerobic treatment can also be used for treating COD, depending on the specific strains developed for the purpose.
Balancing Efficiency and Sustainability
Understanding the processes and differences between aerobic and anaerobic treatment methods is essential for implementing effective and sustainable wastewater treatment strategies. By leveraging the strengths of each method, wastewater treatment facilities can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and promote environmental stewardship for a healthier future.
For tailored solutions to your wastewater treatment challenges, discuss with us, and benefit from our knowledgeable insights.

Industries
Wastewater Treatment
Separation Sciences
Contact
Sign in for latest updates
Stay informed with the latest updates from Diva Envitec! Sign up for our newsletter to receive exclusive news, insights, and case studies directly to your inbox.

Copyright © 2024 Diva Envitec
Terms of Service
Privacy Policy
Industries
Wastewater Treatment
Separation Sciences
Contact
Sign in for latest updates
Stay informed with the latest updates from Diva Envitec! Sign up for our newsletter to receive exclusive news, insights, and case studies directly to your inbox.

